Molecular Structure Of A Carbohydrate
The general empirical structure for carbohydrates is ch2o n. A carbohydrate is a biomolecule consisting of carbon c hydrogen h and oxygen o atoms usually with a hydrogen oxygen atom ratio of 2 1 as in water and thus with the empirical formula c m h 2 o n where m may be different from n.
The scientific term for a single sugar is monosaccharide.
Molecular structure of a carbohydrate. Aldoses have a carbonyl group indicated in green at the end of the carbon chain and ketoses have a carbonyl group in the middle of the carbon chain. Carbohydrates consist of carbon hydrogen and oxygen. The chemical formula for glucose is c 6 h 12 o 6.
In this article we will discuss about the molecular structure of carbohydrates with the help of diagrams. Some carbohydrates also contain nitrogen atoms such as chitin which is found in insect shells. Trioses pentoses and hexoses have three five and six carbon backbones respectively.
Carbon atoms have the ability to bond to four other atoms. They are present in all cellular organisms. A carbohydrate has three or more carbon atoms at least two oxygen atoms and multiple hydrogen atoms.
The double sugar units are known as disaccharides. They are built out of sugar molecules. Proteomics the systematic study of proteins in biological systems has expanded the knowledge of protein expression modification interaction and.
The building blocks of all carbohydrates are simple sugars called monosaccharides. Glycobiology is the study of the structure function and biology of carbohydrates also called glycans which are widely distributed in nature it is a small but rapidly growing field with relevance to biomedicine biotechnology and basic research. Monosaccharides which are simple sugars that serve as fuel molecules as well as fundamental constituents of living organisms are the simplest carbohydrates and are required as energy sources.
It consists of a molecule of d galactose and a molecule of d glucose bonded by beta 1 4 glycosidic linkage. Lactose is a disaccharide found in animal milk. Most carbohydrates are composed entirely of carbon hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
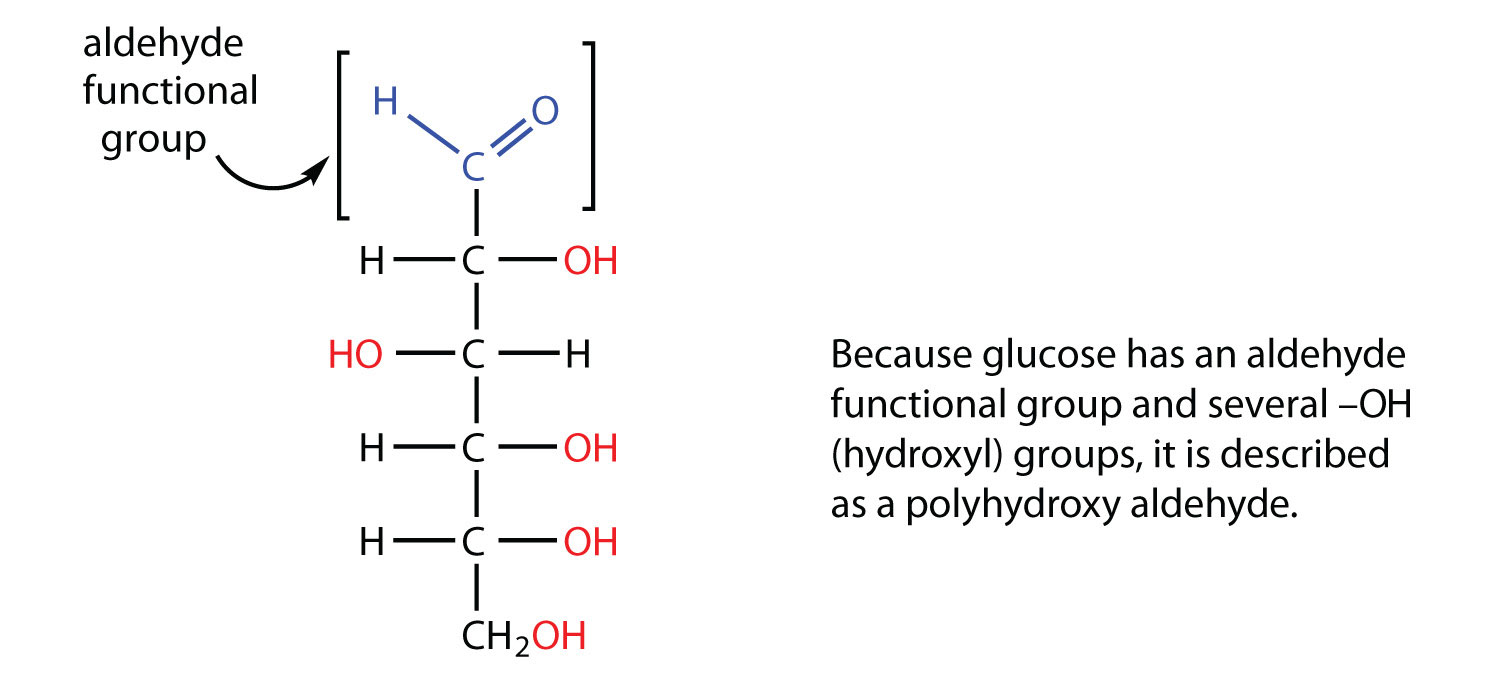
The simple carbohydrates known as monosaccharides contain the three component elements c h and o of which h and o are in the same ratio as that of water. The general empirical structure for carbohydrates is ch 2 o n. They are organic compounds organized in the form of aldehydes or ketones with multiple hydroxyl groups coming off the carbon chain.
All carbohydrates have something in common. Sugar molecules can exist separately as single units or they can join together in pairs to form double sugars. A carbohydrate is a naturally occurring compound or a derivative of such a compound with the general chemical formula c x h 2 o y made up of molecules of carbon c hydrogen h and oxygen o.
The most commonly known ones are perhaps glucose and fructose. When 2 amino acids bond together the two ends of nearby amino acids are released and the carbon called a carboxyl end of one amino acid bonds to the nitrogen end of the adjacent one forming a peptide bond as illustrated below right. Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of carbon hydrogen and oxygen.
Carbohydrates are the most widespread organic substances and play a vital role in all life.
Classification Of Carbohydrates Examples And Structure Of
Biomolecules Welcome To Bio Stud
Structure And Function Of Carbohydrates Biology For Majors I
How Do You Recognize A Carbohydrate Molecule Chemistry Stack
Carbohydrates Ck 12 Foundation
Carbohydrates Biology Visionlearning
What Is The Structure Of Carbohydrates Quora
Carbohydrate Definition Classification Examples Britannica
The Chemical Structure Of Carbohydrates Dummies
Structure And Function Of Carbohydrates Biology For Majors I
Molecular Structures Of Carbohydrates Nana Glc Gal Man
Carbohydrates Biology Visionlearning
Structural Biochemistry Carbohydrates Wikibooks Open Books For
Carbohydrates Biology Encyclopedia Plant Body Process
Structure Of Carbohydrates What Are Carbohydrates Made Of
Carbohydrates From Biomass Sources And Transformation By
Carbohydrates Biology Visionlearning
Classification Of Carbohydrates With Definition Types
5 2 Biomass Carbohydrate Tutorial Egee 439 Alternative Fuels
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gctmvdbmotaw59dstnpcl Iux5pu2zckbro7ifq Pvxe1gy2uxnz Usqp Cau
Carbohydrate Definition Classification Examples Britannica
Structural Biochemistry Organic Chemistry Carbohydrates
Structure And Function Of Carbohydrates Biology For Majors I
Carbohydrates Article Macromolecules Khan Academy
Biological Molecules 5 Sugars Polysaccharides Lipids And Fats
Vr 4904 Diagram Of Carbohydrates Schematic Wiring
Posting Komentar
Posting Komentar